In physics, cryogenics is the production and behavior of materials at very low temperatures. In other words “Cryogenic” means producing or related to low temperatures and all cryogenic liquids are extremely cold. Cryogenic distillation is the process in which nitrogen and oxygen are separated from air. Cryo oxygen gas plant is used for producing oxygen for industrial and medical applications. How does cryogenic distillation work for oxygen nitrogen. Cryogenic distillation technology is used in the manufacturing and fabricating of plant machinery.
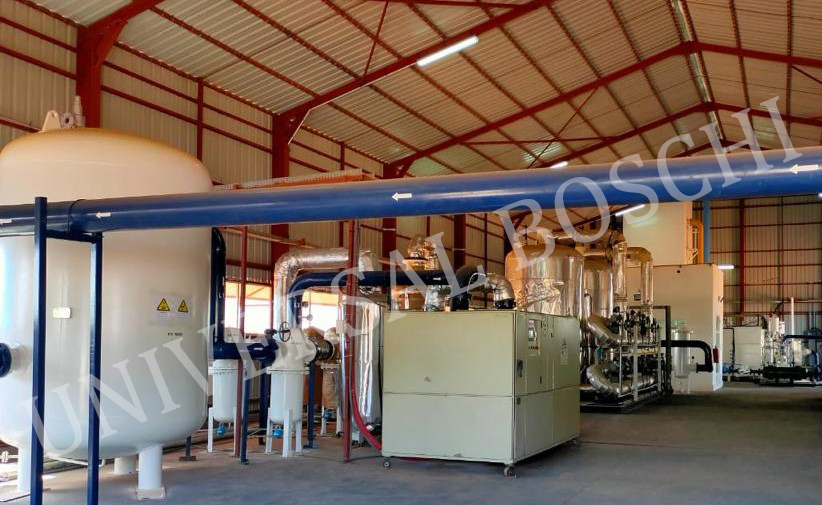
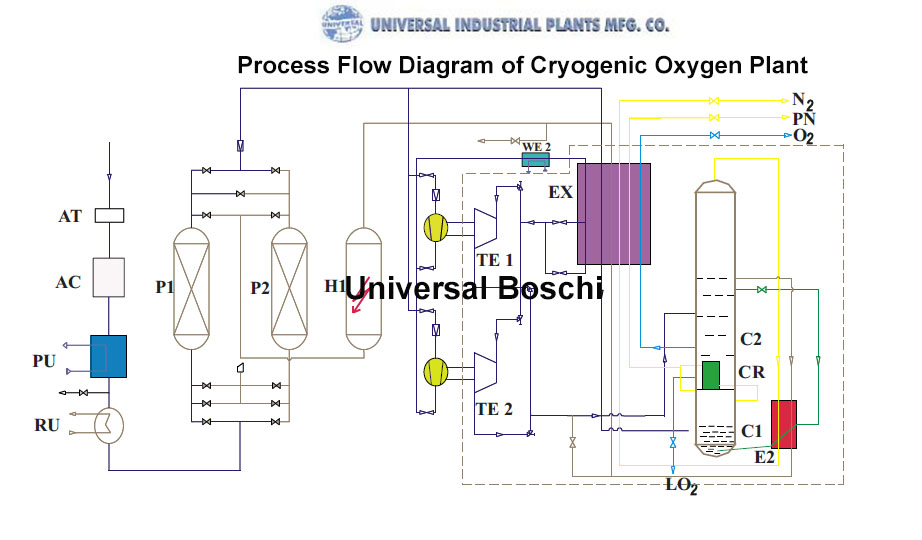

For ensuring smooth working of cryogenic oxygen machinery, it is imperative for tight integration of heat exchangers and air separation columns for maintaining efficiency. Energy for cooling oxygen to cryogenic temperature is obtained by the compression of the air.
In order to get low distillation temperatures cryogenic oxygen plant needs a refrigeration cycle and cold equipment that must be placed within a insulated closure which is commonly known as cold box. However, for getting energy to run refrigeration cycle the latest liquid oxygen plant use expansion turbines.
When the air is compressed, it is passed through a cleanup system where vapor, carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons are eliminated. Afterwards, the compressed air is passed into high pressure distillation column where vaporous oxygen is formed at the top of the column and nitrogen is formed at the bottom of the column.

